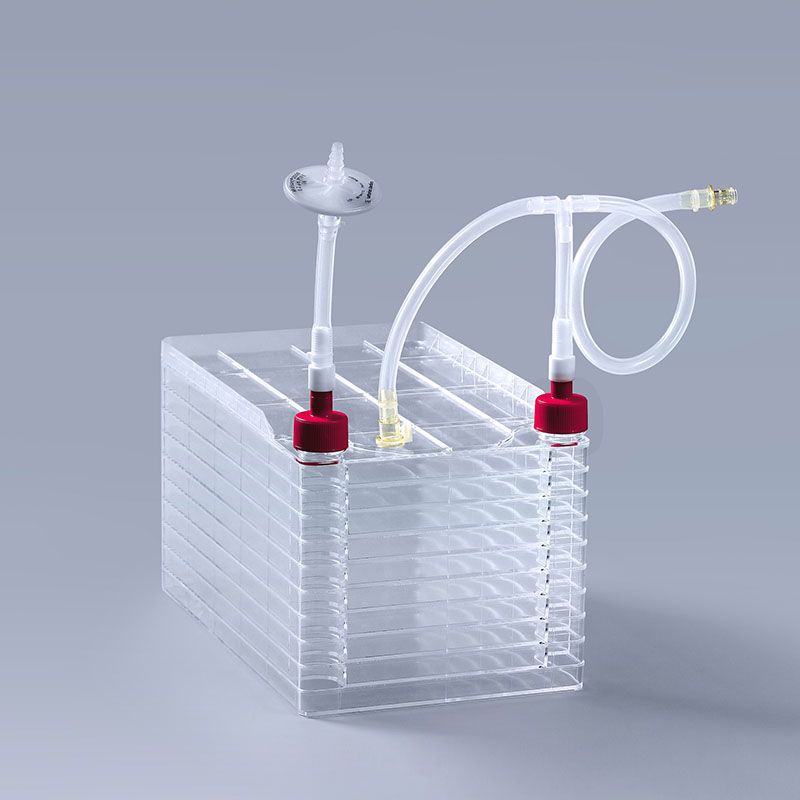
Cell factorys play a crucial role in vaccine production as large-scale cell culture consumables, and they are widely used in the production of the following vaccines:
1. Influenza Vaccine
The production of influenza vaccines typically relies on cell factory systems for large-scale virus cultivation. This process requires rapid proliferation of a significant amount of influenza virus in cell culture media to extract viral antigens for vaccine production. The multi-layer design of cell factory provides sufficient culture area to meet the demands of influenza vaccine production.
2. COVID-19 Vaccine
This is especially true for mRNA and adenovirus vector vaccines, such as Pfizer-BioNTech's BNT162b2 and Moderna's mRNA-1273. The production of these vaccines involves cultivating large quantities of viral vectors or expression systems, and cell factory provide an efficient cell culture environment to support this process.
3. Hepatitis B Vaccine
The production of the hepatitis B vaccine relies on the culture of yeast cells or mammalian cells. Cell factory can produce the necessary HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen) on a large scale for vaccine preparation.
4. Rabies Vaccine
Rabies vaccine production generally uses Vero cells (a monkey kidney cell line) or other cell lines to culture the rabies virus. The cell factory system offers stable and controllable culture conditions, ensuring efficient virus production.
5. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine
The production of HPV vaccines involves using insect cell lines or mammalian cell lines to cultivate the virus or its antigens. The multi-layer culture design of cell factory can support the growth of a large number of cells, meeting the vaccine production requirements.
6. Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
The production of these combination vaccines typically uses chicken embryos or cell culture systems, such as Vero cell lines. Cell factory can provide a suitable culture environment for virus growth, ensuring efficient vaccine production.
Cell factory significantly enhance the production efficiency and capacity of these vaccines by providing a large-scale, efficient, and safe cell culture environment, helping to meet global vaccine demand.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English